Advantages and disadvantages of foreign exchange market - The foreign exchange market, a global marketplace for currency trading, offers numerous advantages and disadvantages that shape its dynamic nature. From the benefits of accessibility and liquidity to the challenges of exchange rate fluctuations and regulatory complexities, understanding these aspects is crucial for navigating this complex market.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the advantages and disadvantages of the foreign exchange market, exploring its market structure, trading strategies, and the impact of technology and innovation. Get ready to embark on a journey through the intricacies of the forex market, where opportunities and risks intertwine.
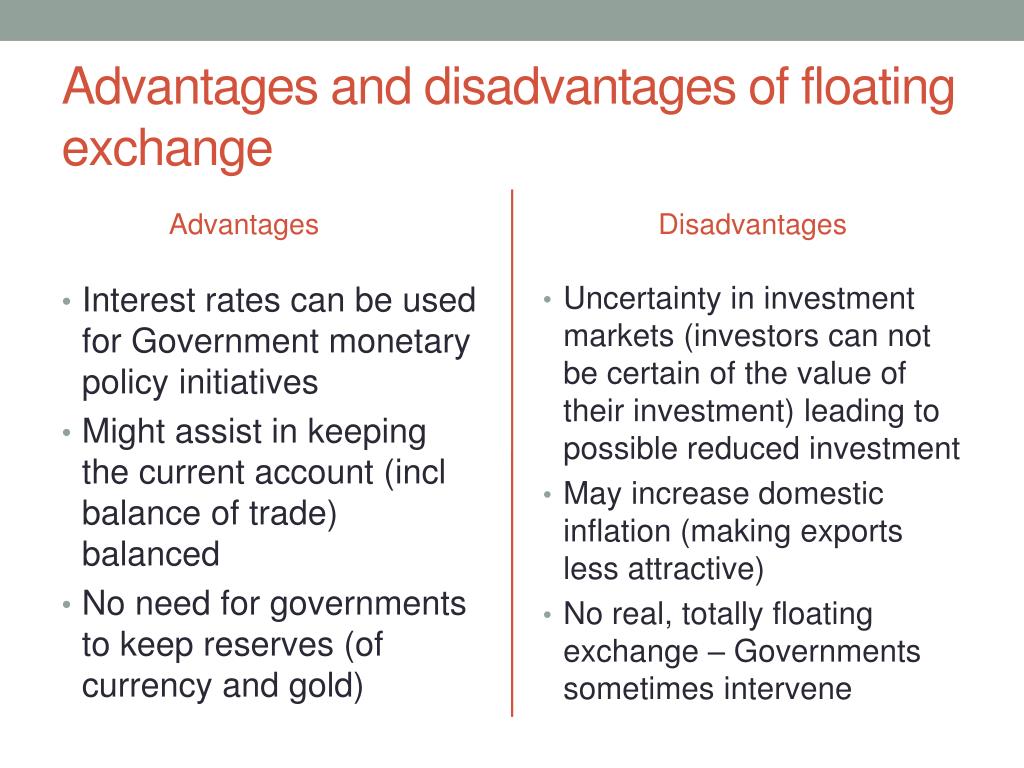
Advantages of Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market offers several advantages that make it an attractive platform for individuals, businesses, and financial institutions. Its global reach and accessibility provide numerous opportunities, while its liquidity and cost-effectiveness contribute to its efficiency.
Global Reach and Accessibility
The foreign exchange market is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with participants from various countries and time zones. This global reach allows for round-the-clock trading, providing participants with access to currencies whenever needed.
Investigate the pros of accepting new york foreign exchange market in your business strategies.
Increased Liquidity
The high volume of trading in the foreign exchange market ensures a deep level of liquidity. This liquidity enables traders to execute large orders with minimal impact on the market price, reducing the risk of slippage and ensuring smooth transactions.
Reduced Transaction Costs
The high competition among foreign exchange brokers and the use of electronic trading platforms have significantly reduced transaction costs. Traders can now access competitive spreads and low commissions, making it more cost-effective to participate in the market.
Diversification and Hedging Risks
Investing in foreign currencies can provide diversification benefits and help reduce overall portfolio risk. By allocating a portion of their assets to different currencies, investors can mitigate the impact of fluctuations in any single currency.
Disadvantages of Foreign Exchange Market

While the foreign exchange market offers numerous advantages, it also poses certain disadvantages that participants should be aware of. These include risks associated with exchange rate fluctuations, regulatory complexities and compliance challenges, and the impact of geopolitical events and economic uncertainties.
Exchange Rate Fluctuations, Advantages and disadvantages of foreign exchange market
Exchange rate fluctuations are inherent to the foreign exchange market and can lead to potential risks for participants. Unfavorable movements in exchange rates can result in losses on investments or transactions denominated in foreign currencies. For instance, if an investor holds a position in a foreign stock and the value of the stock's currency depreciates against the investor's home currency, the investor will experience a loss on their investment.
Regulatory Complexities and Compliance
The foreign exchange market is subject to a complex regulatory environment, varying across different jurisdictions. These regulations aim to ensure market stability, prevent fraud, and protect investors. However, complying with these regulations can be challenging for participants, especially for those operating across multiple jurisdictions. Failure to comply with regulatory requirements can result in fines, penalties, or even criminal charges.
Examine how various participants in the foreign exchange market for us dollars are listed can boost performance in your area.
Geopolitical Events and Economic Uncertainties
Geopolitical events and economic uncertainties can significantly impact the foreign exchange market. Political instability, wars, natural disasters, and economic crises can lead to sharp fluctuations in exchange rates and create volatility in the market. These events can make it difficult for participants to predict exchange rate movements and manage their risk exposure effectively.
Market Structure and Participants
The foreign exchange market is a decentralized global market where currencies are traded. It involves a diverse range of participants, each playing a distinct role in the market's functioning.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of define the meaning of foreign exchange market through case studies.
Market Participants
The main participants in the foreign exchange market can be categorized as follows:
| Participant | Role | Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Banks | Market makers and intermediaries | Facilitate currency trading, provide liquidity, and manage risk |
| Corporations | Multinational companies and businesses | Engage in foreign exchange transactions for international trade, investments, and hedging purposes |
| Retail traders | Individual investors and speculators | Trade currencies for profit or to hedge against currency fluctuations |
| Central banks | Governmental institutions | Influence exchange rates through monetary policy and intervene in the market to stabilize currencies |
The interactions and activities of these participants contribute to the market's liquidity, price discovery, and risk management.
Influence of Central Banks and Government Interventions
Central banks play a significant role in the foreign exchange market through their monetary policies, which influence exchange rates and market sentiment. They can intervene in the market to stabilize currencies, manage inflation, or support economic growth.
Government interventions, such as currency controls or exchange rate pegs, can also impact the market structure and participants' activities.
Trading Strategies and Instruments
The foreign exchange market offers a wide range of trading strategies and instruments to meet the needs of different market participants. These strategies and instruments vary in terms of risk, complexity, and potential return.
Some of the most common trading strategies include:
- Spot trading: Involves the immediate buying and selling of currencies at the current market rate.
- Forward contracts: Agreements to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a specified exchange rate on a future date.
- Options: Contracts that give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a specified exchange rate on or before a specified date.
The foreign exchange market also offers a variety of instruments, including:
- Currency pairs: The most common type of foreign exchange instrument, which represents the exchange rate between two currencies.
- Indices: Baskets of currencies that represent the value of a particular currency against a group of other currencies.
- Futures: Contracts to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a specified exchange rate on a future date.
Traders use both technical and fundamental analysis to make informed trading decisions. Technical analysis involves studying historical price data to identify patterns and trends that may indicate future price movements. Fundamental analysis involves studying economic and political factors that may affect the value of currencies.
Technology and Innovation: Advantages And Disadvantages Of Foreign Exchange Market

The foreign exchange market has witnessed a significant transformation in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and innovation. Electronic trading platforms and algorithmic trading have revolutionized the way currencies are traded, enhancing market efficiency, transparency, and accessibility.
Electronic Trading Platforms
- Electronic trading platforms have replaced traditional over-the-counter (OTC) trading methods, enabling traders to execute orders directly through online platforms.
- These platforms provide real-time market data, liquidity, and advanced order execution capabilities, facilitating faster and more efficient transactions.
- Examples include the EBS (Electronic Broking Services) and Thomson Reuters Matching, which account for a substantial portion of global FX trading volume.
Algorithmic Trading
- Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading, involves using computer programs to execute trades based on predefined rules and strategies.
- Algorithms analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades automatically, reducing human intervention and potential biases.
- High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic trading that employs sophisticated algorithms to exploit short-term price movements.
Improved Market Efficiency and Transparency
- Technology has greatly improved market efficiency by automating trading processes and reducing execution times.
- Electronic trading platforms provide transparent pricing and order matching, allowing traders to make informed decisions and reduce information asymmetry.
- Algorithmic trading contributes to market liquidity by executing large orders quickly and efficiently, reducing bid-ask spreads and improving price discovery.
Emerging Trends and Future Advancements
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are gaining traction in the FX market, enabling traders to analyze large datasets and identify trading patterns.
- Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize FX settlement by providing a secure and transparent platform for clearing and settlement.
- Cloud computing offers scalability and flexibility for FX trading platforms, allowing them to handle high trading volumes and provide real-time data analysis.
Last Recap
The foreign exchange market presents a complex and ever-evolving landscape, offering both opportunities and challenges for participants. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages Artikeld in this guide, traders and investors can make informed decisions, navigate market complexities, and harness the potential of the forex market.
As the market continues to adapt to technological advancements and geopolitical shifts, staying abreast of these dynamics will be essential for success in the ever-changing world of foreign exchange.
